Healthcare AI Tools Market Landscape
The global artificial intelligence in healthcare market, valued at approximately $26.57 billion in 2024, is experiencing unprecedented growth with projections indicating expansion to $187.69 billion by 2030 at a compound annual growth rate of 38.62%. Healthcare AI tools can be broadly classified into three primary categories: machine learning applications for predictive analytics and diagnostics, natural language processing systems for clinical documentation and data extraction, and robotic process automation for administrative task optimization. Current adoption statistics reveal that 86% of healthcare organizations are already extensively implementing AI technologies across various operational domains, with many reporting a return on investment of $3.20 for every dollar invested within 14 months. These tools are demonstrating significant impact in medical imaging analysis, electronic health record management, and clinical decision support systems, with particular emphasis on improving diagnostic accuracy and operational efficiency. The market is predominantly led by North America, which accounted for over 54% of global revenue share in 2024, driven by advanced healthcare infrastructure, substantial R&D investments, and supportive regulatory frameworks. As healthcare systems worldwide continue to grapple with workforce shortages and rising patient volumes, AI tools are increasingly positioned as essential components in addressing these systemic challenges while enhancing patient care outcomes.
Diagnostic AI Applications in Medical Imaging and Pathology
Diagnostic AI tools have demonstrated measurable improvements in accuracy and efficiency across various medical specialties, with radiology and pathology showing particularly robust adoption rates in clinical settings. In neuroimaging applications, Aidoc’s intracranial hemorrhage detection system achieved 96.2% sensitivity and 93.3% specificity in retrospective studies, reducing scan view delay by 89.6% for outpatient cases at academic medical centers while maintaining high diagnostic reliability across diverse patient populations. PathAI’s digital pathology platform has shown 70% agreement rates for ballooning grade assessment compared to pathologist consensus, addressing longstanding challenges in histopathological interpretation consistency that previously resulted in significant inter-observer variability among specialists. These implementations highlight how AI serves as a complementary tool rather than a replacement, with Massachusetts General Hospital reporting that AI-assisted radiologists maintained their diagnostic accuracy while reducing interpretation time for complex cases by approximately 30%, allowing clinicians to focus on higher-value decision-making activities.
Treatment Planning Support AI Tools Real Application Cases
Treatment planning AI tools are increasingly demonstrating clinical utility by integrating genomic data with evidence-based guidelines to recommend personalized therapeutic approaches across diverse cancer types. IBM Watson for Oncology achieved 90% concordance with tumor board recommendations across 638 breast cancer cases in India, reducing data analysis time from 20 minutes to just 40 seconds while identifying clinically actionable information in approximately 30% of cases that human reviewers initially missed. Tempus’ comprehensive genomic profiling platform revealed that 82% of fusion-positive NSCLC patients received matched targeted therapy, with those receiving appropriate treatment showing significantly longer real-world overall survival compared to non-recipients (HR=0.13, p<0.001). Recent studies demonstrate that AI-assisted clinical summaries yield accurate treatment plans in 90% of cases when input data is accurate, with specialists preferring AI-assisted approaches over human-only methods for faithfulness, completeness, and succinctness while achieving up to 22.2x speed improvements in summarization time.
Real-World Patient Management AI Tool Applications
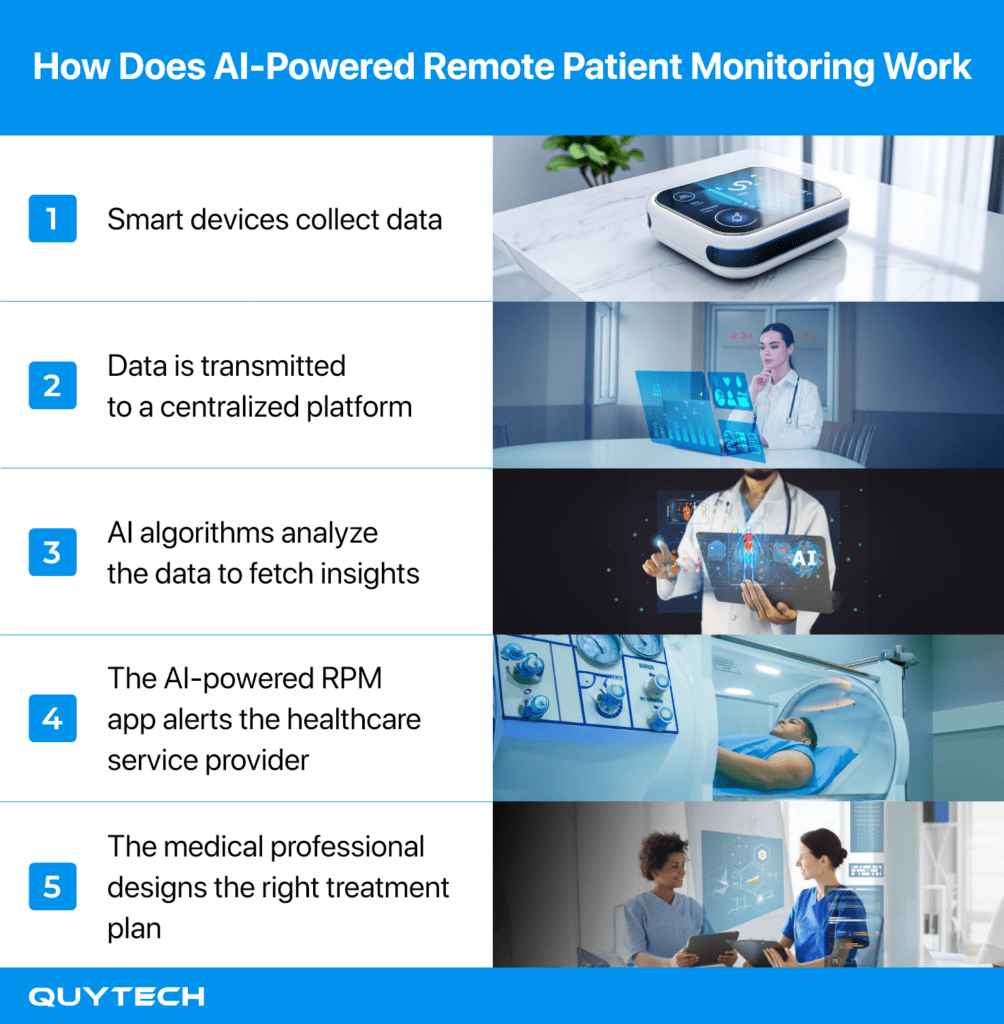
Patient management AI tools are demonstrating significant value in healthcare settings through real-world implementations that enhance monitoring, support, and predictive capabilities across diverse clinical environments. Remote patient monitoring systems integrated with artificial intelligence algorithms now enable continuous tracking of vital signs and early detection of health deterioration for chronic disease patients, with studies showing up to 25% reduction in hospital readmissions for heart failure patients using these technologies. Virtual health assistants provide 24/7 patient support through conversational interfaces, handling appointment scheduling, medication reminders, and basic medical inquiries while reducing administrative burden on clinical staff by approximately 30% according to hospital implementation data. Predictive analytics tools specifically designed for readmission risk assessment have achieved accuracy rates exceeding 85% in identifying high-risk patients, allowing healthcare providers to implement targeted interventions that have reduced 30-day readmission rates by as much as 25% in multiple hospital systems while improving resource allocation and patient outcomes.
Healthcare Administrative Workflow Optimization Through AI

Administrative burdens consume up to 55% of clinicians’ time, significantly contributing to burnout while diverting attention from direct patient care, but AI-driven solutions are demonstrating substantial improvements in workflow efficiency across healthcare settings. AtlantiCare’s implementation of Oracle Health’s Clinical AI Agent has achieved a 40-50% reduction in documentation time, saving clinicians approximately five minutes per patient encounter and nearly ten minutes in overall EHR usage, with over 40,000 clinical notes generated since January through passive listening technology that creates draft documentation for provider review. Similarly, Amplify Care’s evaluation of AI scribes revealed clinicians spent 69.5% less time documenting in simulated environments and reported three fewer hours weekly on after-hours charting, with 68% noting reduced administrative burden and 55% experiencing decreased stress levels. Laboratory professionals have also embraced automation, with 89% agreeing their facilities require these technologies to meet growing demands and 91% believing AI tools can address unmet patient care challenges, particularly as staffing shortages lead to temporary lab closures that delay critical testing relied upon for 70% of medical decisions.
Healthcare AI Implementation Critical Factors
The successful integration of artificial intelligence into healthcare systems requires careful navigation of multiple interconnected considerations that directly impact both patient outcomes and operational sustainability. Recent data reveals that 47 percent of physicians rank increased oversight as the top regulatory action needed to build trust in AI adoption, while 68 percent of organizations expect AI to transform compliance management within three years, highlighting the growing recognition of governance frameworks as essential components of implementation strategy. Healthcare institutions must balance the substantial initial investment requirements, which can range from $40,000 for basic AI functionality to well over $100,000 for comprehensive custom solutions, against demonstrated returns where 64 percent of organizations implementing generative AI have already quantified positive ROI through improved administrative efficiency and clinical productivity. The AMA’s eight-step governance framework emphasizes executive accountability, working group formation, current state assessment, policy development, vendor evaluation processes, implementation planning updates, oversight mechanisms, and organizational readiness as critical structural elements for sustainable AI integration that addresses both technical and human factors in healthcare environments.